Description
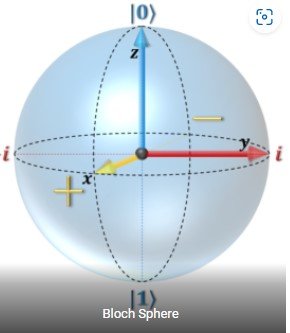
The two main quantum resources are quantum bits, or qubits, and quantum gates. Qubits can take on any complex value between 0 and 1. That is a qubit, 𝑞, can be defined as |𝑞⟩ = 𝛼|0⟩ + 𝛽|1⟩ where 𝛼 and 𝛽 are complex probabilities, and |0⟩ and |1⟩ represent the computational basis states. This can be visually represented by the Bloch sphere on the right. Quantum gates can act on a single qubit at a time, or on multiple qubits at once, which is called quantum entanglement. Classical gates can be modeled with quantum gates, but there are a few quantum gates which cannot be classically modeled. One of these gates is the Hadamard gate which when applied to a basis state, puts the qubit into superposition.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.